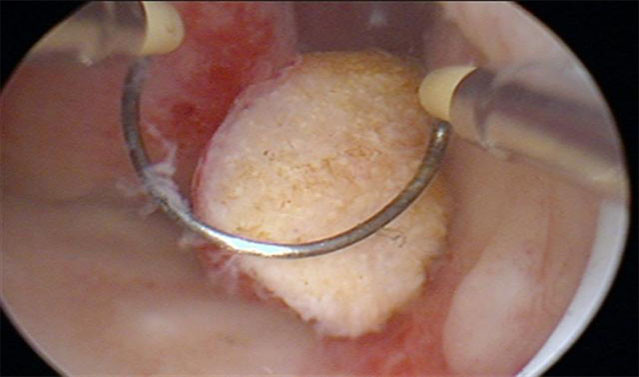
Hysteroscopy is a method that provides observation by accessing into the uterus with a thin and special tubular camera, allowing to perform procedures for both diagnostic and theurapeutic purposes. Images are detailedly examined with the help of a monitor. The tubular device in the camera system inserted into the uterus is defined as hysteroscope.
Hyteroscopy is a technique carried out using local anesthesia during examination and general anesthesia in operating room environment. It is performed especially within 1 week after the end of woman’s menstruation. This period is the most suitable period to be able to visualize inside of the uterus.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy:
It is used to identify problems such as myoma, adhesions and polyps present inside of the uterus. In some cases, it is sufficient alone, while in some cases, it is used in combination with laparoscopy.
In which cases is diagnostic hysteroscopy carried out?
- Infertility
- Excessive menstruation and irregular menstrual bleeding
- In recurrent miscarriage cases
- In cases of adhesion present in the uterus
- In cases of intrauterine devices that are not possible to remove or are displaced in the uterus
- In ultrasound examination to observe areas such as myoma and polyp
In which cases is surgical (or operative) hysteroscopy carried out?
It is used to remove lesions such as polyp, myoma present in the uterus, to correct the components and to treat current adhesions.
What are the risks that may occur due to hysteroscopy?
Actually, hysteroscopy is a safe treatment method. However, in some cases, uterine injury, excessive bleeding, intrauterine inflammation, injury to the cervix and a number of complications associated with anesthesia administered may occur.
How is hysteroscopy performed?
In some cases, the patient can be given drug to be administered orally or vaginally to obtain sufficient openness in the cervix before starting to perform hysteroscopy. Hysteroscopy is performed under spinal or general anesthesia by placing the patient in a position as if gynecological examination is performed.
The patient undergone hysteroscopy is discharged a few hours after the procedure or the next day. Vaginal bleeding and pain in the form of cramp may arise one or two days after the procedure. But this is not something to be afraid of.
If complications such as
- Excessive bleeding
- Unbearable abdominal pain
- Fever
develop, it would be beneficial to reconsult doctor.